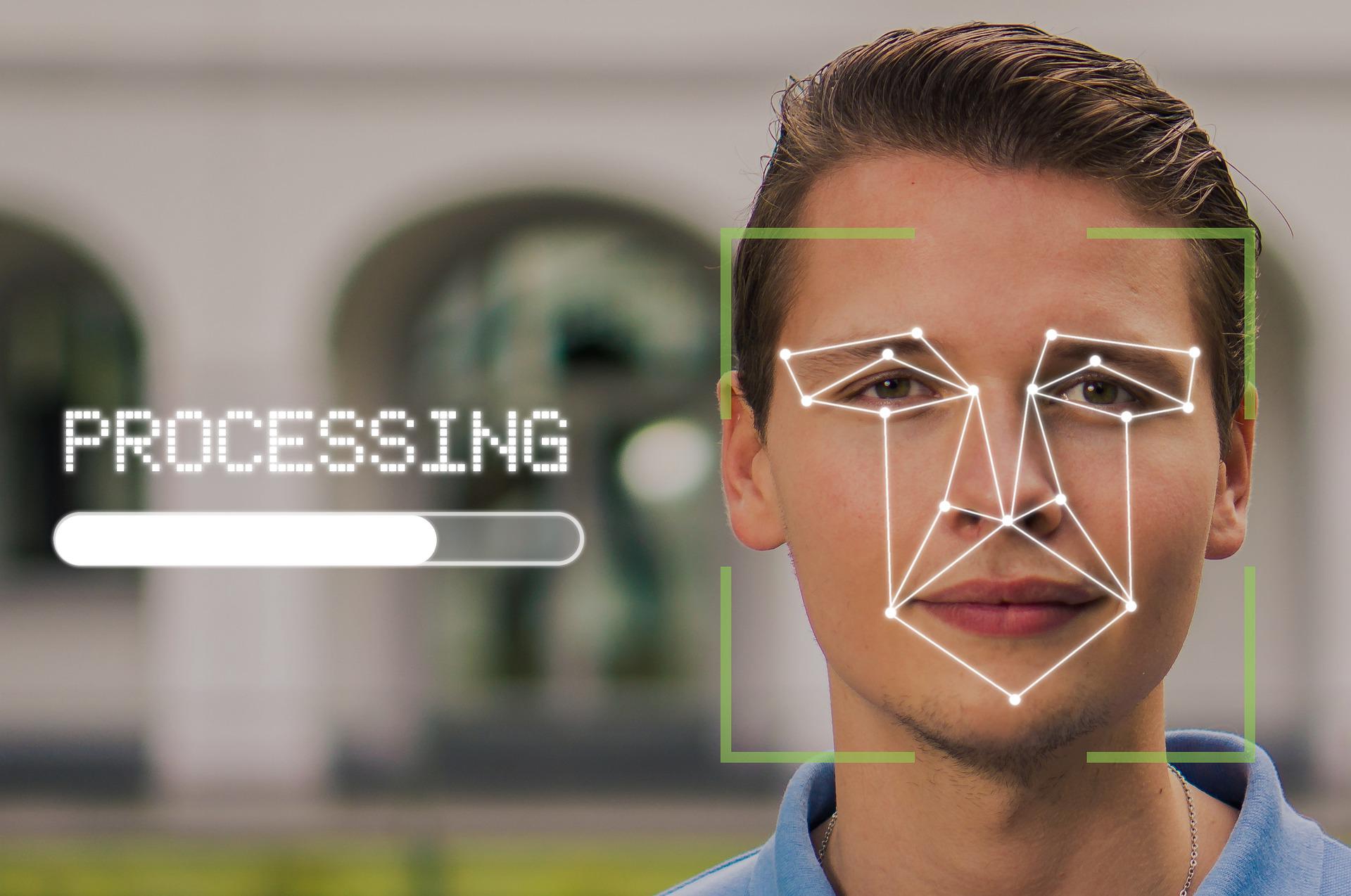
Expensive smartphones and laptops already have biometric sensors as a more advanced form of security measure. These sensors authenticate users by their unique physical characteristics. However, if you think that biometric technology is the final and the most secure authentication technology, that it isn’t the case.
Here are common problems that you may find with biometric technology:
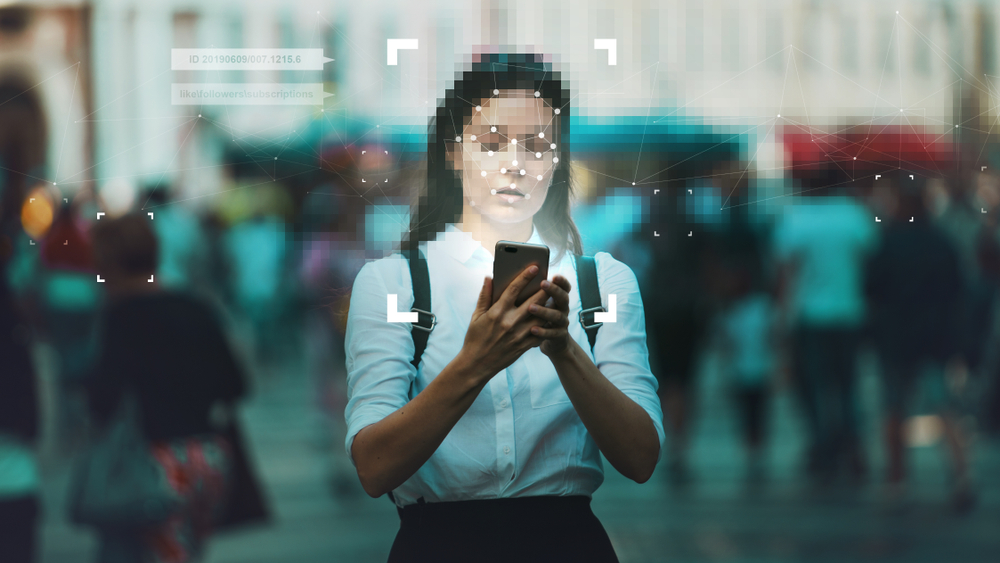

1. Biometric data can be stolen
Once your biometric characteristics are digitized, the data must be stored somewhere. Unfortunately, the digital versions of your biometrics can be stolen and misused. The mapped details of your fingerprints, retina and facial profiles can be used to hack many biometric security systems. If your biometric information has been compromised, there’s no way to change that. It’s easy to change your password or PIN regularly, but there’s no way to change your biometric data. If you have been working in multiple companies in the past, you might already give your fingerprints details to these organizations. Your biometric details should be completely removed once you resign from the company. Your biometric details can be simply neglected and stashed in the company servers and no one really care if they are stolen by a bad employee.
2. You can fool biometric sensors
Hackers are always developing ways to fool the biometric system. Some fingerprint sensors have temperature scanner to prevent unauthorized access with fake fingerprints. However, it is possible to bypass this feature by blowing hot air across the sensor. Biometric system vendors always promise that their scanners are difficult to fool, but it’s not a complete guarantee.
3. It’s sometimes inaccurate
It’s wrong to assume that biometrics are always accurate. Although your fingerprint is unique, the way it is scanned, processed and analyzed may not be precise. In some biometric solutions, information isn’t measured and stored in high detail. As an example, fingerprints are interpreted digitally as quantized “valleys and ridges”. It means that there’s a degree of information loss when your fingerprint is being digitized. There’s actually a chance that another person with nearly identical fingerprint can be authenticated and granted access. It’s especially true for low-cost fingerprint scanner that doesn’t digitize fingerprint information with good resolution. Not all businesses or organizations are willing to invest enough on biometric capabilities.
4. Biometric data are not secret
Unlike private encryption key or password, your biometric data are all over the place. Your face and fingerprints can be captured by anyone around you. If your biometric details are so easily accessible and visible, this may lead to a real issue. There are many security concerns if the world goes largely biometric. Hackers will start stealing, modifying and selling biometric data. It is possible for them to do remote logons using the stolen biometric data. If your biometric data have been compromised and sold by hackers, it is possible that you are no longer eligible for accessing many systems, although it’s not your fault. In the end, usernames and passwords are still the most secure and convenient security method, if they are complex enough and changed regularly.